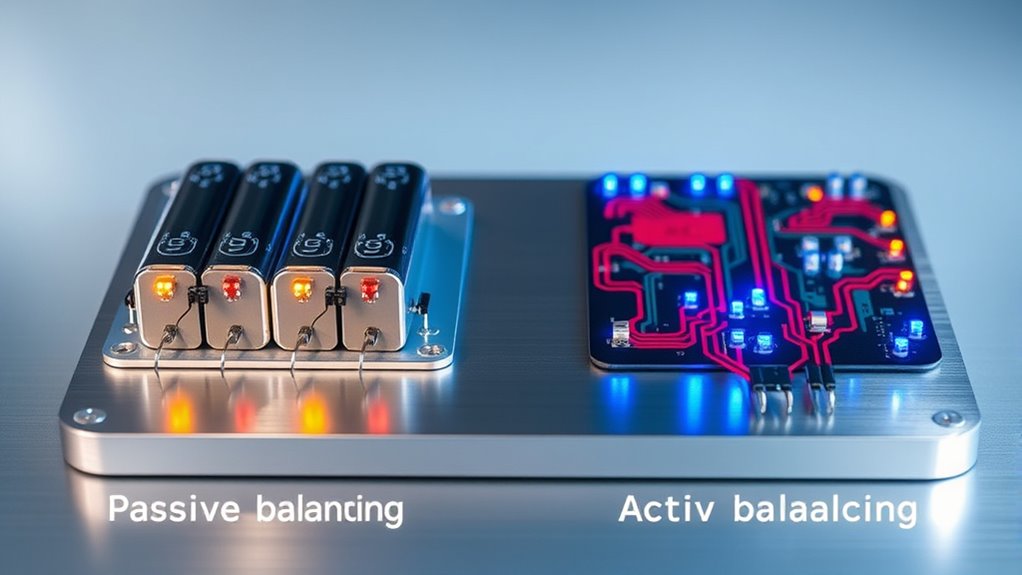
Passive balancing is simple and low-cost, using resistors to dissipate excess energy as heat, but it wastes energy and can limit battery lifespan over time. Active balancing transfers energy between cells with inductors or capacitors, improving efficiency and extending battery life, though it’s more complex and costly to implement. If you want to discover which method best fits your needs, exploring the pros and cons can help you make an informed choice.
Key Takeaways
- Passive balancing is simpler and lower-cost but dissipates excess energy as heat, reducing efficiency.
- Active balancing redistributes energy between cells, improving efficiency and extending battery life despite higher complexity.
- Passive systems are suitable for small or low-demand applications, whereas active systems excel in high-capacity, demanding setups.
- Active balancing minimizes energy waste, leading to better long-term reliability and battery longevity.
- Passive balancing involves less maintenance but may cause more frequent battery replacement due to energy loss.
When it comes to maintaining the health and performance of batteries, understanding the difference between passive and active balancing is essential. Both methods aim to ensure each cell in a battery pack operates at the same voltage, but they do so through different approaches, impacting battery longevity and system complexity. Recognizing these distinctions helps you choose the right solution for your application, whether it’s for electric vehicles, solar energy storage, or portable devices.
Passive balancing works by dissipating excess energy from higher-voltage cells as heat, usually through resistors or other dissipation components. It’s straightforward and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for many systems. However, because it wastes energy as heat, it can limit battery longevity over time, especially if the system operates frequently at high charge levels. The system complexity is relatively low, meaning it’s easier to implement, maintain, and troubleshoot. This simplicity is a significant advantage if you want a reliable, low-cost solution without requiring complex control circuitry. Additionally, passive balancing is often preferred for smaller or less demanding applications due to its simplicity and affordability.
Passive balancing dissipates excess energy as heat, offering a simple, low-cost solution but potentially limiting battery lifespan.
Active balancing, on the other hand, transfers energy from higher-voltage cells to lower-voltage ones, using inductors, capacitors, or transformers. This process is more efficient because it minimizes energy loss, which can extend your battery’s lifespan. By redistributing energy instead of wasting it, active balancing can improve overall system efficiency and reduce the need for frequent charging or replacement. The trade-off is that active systems tend to be more complex, involving sophisticated circuitry and control algorithms. This complexity can increase initial costs and maintenance efforts, but it offers better performance and longer-term reliability, especially in large or high-demand battery packs.
If your priority is maximizing battery longevity and system efficiency, especially in high-capacity or high-performance applications, active balancing often makes sense despite its higher complexity. It allows your batteries to operate more evenly over time, reducing stress on individual cells and preventing premature degradation. Conversely, if your application demands a simple, budget-friendly solution with less maintenance, passive balancing might be sufficient. It’s easier to implement and requires less ongoing oversight, but you should be mindful of its energy waste and potential impact on battery lifespan over the long run. Understanding the differences in balancing methods helps in making an informed decision tailored to your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Balancing Method Is More Cost-Effective Long-Term?
Passive balancing is typically more cost-effective long-term because it requires lower initial investment and simpler installation, leading to cost savings. Although active balancing offers better performance and efficiency, it involves higher setup complexity and maintenance costs. If you prioritize long-term savings and easier maintenance, passive balancing is usually the better choice. However, if you need higher precision and performance, consider active balancing despite the higher upfront costs.
How Does Temperature Impact Passive and Active Balancing?
Temperature impacts passive and active balancing through thermal effects that influence their efficiency. In passive balancing, higher temperatures can cause uneven heat distribution, reducing effectiveness and risking thermal runaway. Active balancing benefits from better temperature regulation, maintaining consistent thermal conditions across cells, which improves performance and safety. You should consider temperature management strategies for both methods to optimize battery life, ensuring thermal effects don’t compromise balancing efficiency or safety.
Can Balancing Methods Be Combined for Better Performance?
Yes, you can combine balancing methods for better performance through hybrid strategies. These strategies integrate passive and active balancing, leveraging the strengths of both to optimize battery health and efficiency. By applying advanced optimization algorithms, you guarantee more precise control, reduce energy waste, and extend battery lifespan. This approach allows you to adapt dynamically to different conditions, maximizing the benefits of both methods and achieving a balanced, reliable system.
What Are the Maintenance Requirements for Each Balancing Type?
You need to regularly inspect passive balancing systems to guarantee components like resistors and capacitors are functioning properly, which helps maintain voltage regulation and energy efficiency. Active balancing systems require more complex maintenance, including checking power electronics and control algorithms, to optimize energy flow and keep voltage levels stable. Both types benefit from routine cleaning and testing to prevent faults, ensuring reliable operation and sustained efficiency over time.
How Do Balancing Methods Affect Battery Lifespan?
Your choice of balancing method directly impacts your battery’s lifespan. Active balancing, with its precise energy redistribution, minimizes stress on the cells, preserving battery chemistry and boosting energy efficiency. Meanwhile, passive balancing can cause uneven wear over time, shortening your battery’s life. If you want longevity and ideal performance, actively balancing your batteries keeps them healthier longer, ensuring you get the most out of every charge.
Conclusion
While passive balancing is simple and cost-effective, it can waste energy and slow down the process. On the other hand, active balancing efficiently equalizes cell voltages quickly, but it comes with higher complexity and initial costs. Choosing between them depends on your priorities: save money or optimize performance. Ultimately, passive and active balancing each have their strengths and weaknesses—like a budget-friendly sedan versus a high-performance sports car. Your decision hinges on what matters most to you.









